What Is the Difference Between a 4 Cylinder and 6 Cylinder Engine?
Everything you need to know about a four-cylinder and six-cylinder engine that you may see as you browse vehicles.
 BMW Group
BMW Group
The difference between a four-cylinder and six-cylinder engine is important to understand when you're shopping for a car. It isn't solely a matter of power: It's also one of fuel efficiency, which may matter to drivers with longer commutes. Here's what you need to know about the types of four-cylinder and six-cylinder engines that you may see as you browse vehicles.
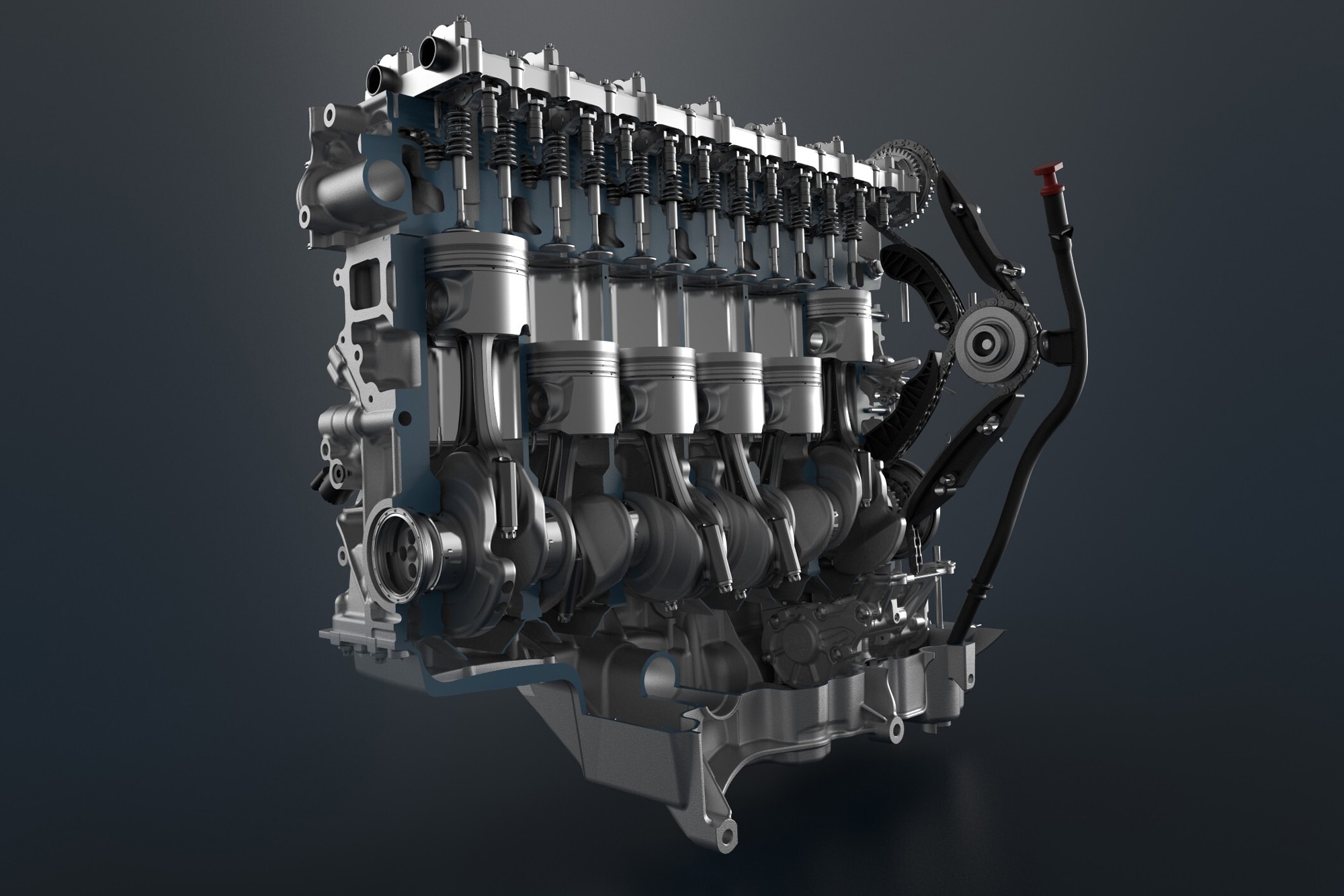
What Is a Cylinder, Anyway?
The cylinders in engines are empty chambers. In each cylinder, there is a solid metal tube called a piston. The pistons move up and down in the cylinders to turn fuel into the power that makes your car move. The process starts when the piston moves down and an inlet allows fuel into the cylinder to mix with air. It continues when the piston moves back through the cylinder to compress this air-and-fuel mixture (making it combustible), and then uses a spark plug to ignite the mixture with a spark. This spark pushes the piston back in the other direction, where an outlet valve opens to release the exhaust gases. The process happens very quickly, in a repeated pattern, inside each cylinder to generate power.
The less-common diesel engine uses an almost identical process, but without the use of a spark plug to ignite the mixture. The engine compresses the mixture of diesel and air until it ignites from the pressure. Both four- and six-cylinder diesel engines are available, but the comparisons between the two follow roughly the same rules as gasoline engines.
Four-Cylinder Engines Versus Six-Cylinder Engines
As their names imply, the biggest difference between a four-cylinder and six-cylinder engine is the number of cylinders they contain. A four-cylinder engine typically offers better fuel economy because it's smaller than a six-cylinder engine and uses less fuel. Its smaller size also means it weighs less, which can improve overall vehicle performance.
However, if an engine is turbocharged, then that rule changes. A turbocharger increases the oxygen flow to the engine, which increases power. Turbocharged four-cylinder engines can be a happy medium for consumers — they offer better performance than their non-turbocharged variants and better fuel economy. You can also get turbocharged six-cylinder engines, which offer similar performance and fuel economy improvements compared to a non-turbocharged six-cylinder engine.
Types of Four-Cylinder and Six-Cylinder Engines
As you browse for cars, you may encounter different types of four- and six-cylinder engines. Both engines are available as inline engines, which may be seen written as inline-four, I-4, or straight-four. An inline six-cylinder may be written as an inline-six, I-6, or straight six. Each name variation, however, means the same thing: The number in the name indicates the number of cylinders, and "inline" means that the cylinders are mounted in a straight line.
Inline is the most common orientation for a four-cylinder engine, but it's not the only one. Several automakers use an H-4, also known as a boxer or flat-four. This puts two cylinders on each side of the engine in the shape of an H. An I-4 is an engine that's most common in smaller vehicles rather than vehicles with high horsepower.
When the engine is an inline-six, it has the same layout as an inline-four, but with two more cylinders. It provides more horsepower than its four-cylinder counterpart, but it's not as commonly used. That's because six cylinders in a row take up a lot of space in the engine compartment, making another engine layout—the V6—a more popular choice when there are more than four cylinders.
A V6 engine splits the cylinders into two sets of three, arranged in a V-pattern on each side of the engine. Mounting cylinders at an angle in the engine compartment makes the engine more compact, and has the benefit of a better center of gravity and less vibration, providing a smoother ride with improved handling.
Which Type of Engine Is Better?
It's not so much that one of these engines is better than the other, but that each offers its own pluses and minuses. A four-cylinder engine fits well in smaller cars and offers great fuel efficiency, but it lacks the power of a six-cylinder. Adding turbocharging improves fuel economy and performance without taking up the space of a larger engine.
A six-cylinder has more power, but it also uses more gas. These are available turbocharged, too, which adds to their performance and improves their fuel economy. The best engine choice for you, however, is the one with the capability and performance that fits your needs.



